In the vast ecosystem of Search Engine Optimization (SEO), crawling is one of the most fundamental yet often misunderstood concepts.
Every time you search something on Google, you’re relying on an underlying process that started with crawling. But what exactly does it mean for a website to be “crawled”?
Crawling is the process by which search engines like Google, Bing, and others use automated bots known as “crawlers” or “spiders” to scan websites across the internet.
These bots systematically browse web pages, gather information about their content, structure, and links, and store it for indexing. It’s the first step in getting your website visible in search engine results, making it a cornerstone of SEO.
Understanding how crawling works, what affects it, and how to optimize for it can help businesses and digital marketers ensure their websites are discoverable and relevant to users.
Proper crawling and indexing increase the chances of a website appearing in search results, thus improving its visibility, traffic, and overall online presence.
In this blog, we’ll explore how crawling works and offer practical tips to optimize your website for search engine bots.
What Is Crawling in SEO?
Crawling in SEO is the process by which search engines use automated bots, known as “crawlers” or “spiders,” to explore and discover new content on websites.

These bots navigate through web pages by following links from one page to another, gathering information about the content, structure, and relationships between pages.
Once the data is collected, it’s sent back to the search engine for further processing.
Crawling plays a crucial role in the SEO ecosystem because it is the first step in making a website discoverable by search engines.
Without crawling, a website’s content would remain invisible to search engines and, by extension, users impacting benefits of SEO such as visibility, traffic, and online authority.
This process ensures that search engines have access to the most up-to-date and relevant content to show in search results, helping websites reach their target audience.
Crawling is often confused with indexing and ranking, but each step has a distinct role:
- Crawling refers to the discovery of web pages by search engines through bots that explore the internet.
- Indexing is the next step, where search engines store and organize the information gathered during crawling. It’s like adding a webpage to a vast digital library.
- Ranking comes after indexing, where search engines determine the relevance and quality of indexed pages and rank them accordingly based on specific factors like keywords, content quality, and backlinks.
What is a Crawler/Bot/Spider?
A crawler, also known as a bot or spider, is an automated program used by search engines to discover and index content across the web.

These bots are essential for gathering information from websites, which search engines use to populate search results. The most famous crawlers include Googlebot (for Google), Bingbot (for Bing), and Yahoo Slurp (for Yahoo), each designed to systematically visit web pages, retrieve content, and index it for future retrieval in search queries.
Learning about how crawlers interact with websites is a foundational step for anyone researching how to get into digital marketing successfully.
How Does a Crawler Work in SEO?
Crawling in SEO requires the action of a crawler, but how exactly does a crawler work? A crawler, also known as a web spider, is an automated program created by search engines to scan the entire web for data.
Its primary purpose is to evaluate content and store relevant information in databases and indexes to optimize search engine performance.
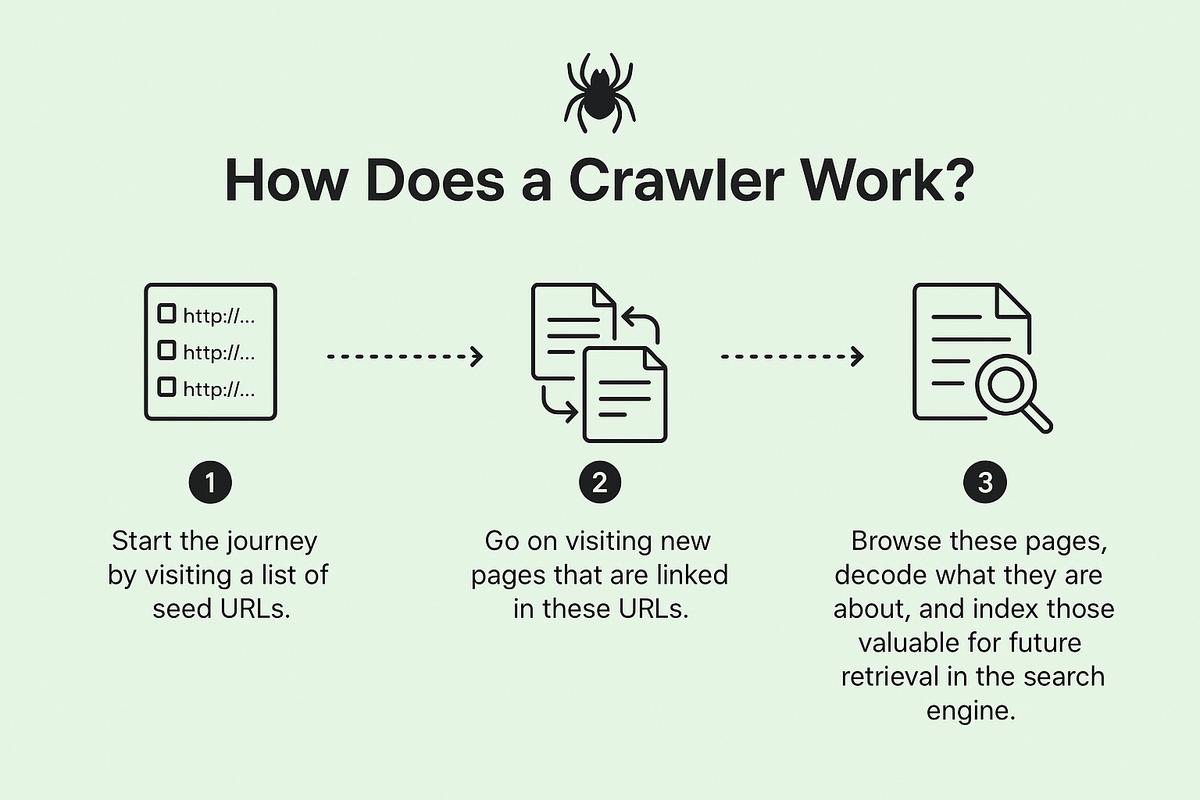
When a user types a query into the search bar, the search engine accesses its index of web pages to display results that match the user's search intent or the keyword used.
The crawler is responsible for discovering and collecting data that can later be indexed and ranked in search results.
It's important to note that crawling in SEO does not happen the same way for every website. Web pages with an easily accessible structure are easier for the crawler to navigate compared to those that rely heavily on complex HTML code or have poor internal linking.
This is why the structure of a website plays a crucial role in successful SEO crawling.
In the world of SEO, crawling refers to the process by which search engine bots visit web pages, collect data, and store it for indexing.
The crawler systematically searches, discovers, and gathers data on the web, following links from page to page, ensuring that the most relevant and high-quality content is indexed for search results.
Key Actions of Crawling in SEO:
- Search Data: Crawlers scan for new or updated content that can be indexed.
- Discover Data: The crawler identifies links to new web pages.
- Collect Data: Data from each page is extracted and sent back to the search engine’s database for indexing.
If you're asking "what is crawling in SEO?", it's the process of ensuring that web pages are explored, understood, and included in the search engine’s index. This is essential for driving traffic to your website.
For website owners, understanding how to control SEO crawl is important. By utilizing techniques such as robots.txt files, sitemaps, and noindex directives, you can guide crawlers and control which pages are crawled or excluded from indexing.
Explore Our Digital Marketing Services!
Differences Between Good Bots (Search Engines) and Bad Bots (Scrapers)
Good bots and bad bots serve different roles on the web, with distinct behaviors and impacts on websites. Below is a comparison highlighting their key differences.
Here’s a table summarizing the differences between good bots and bad bots:
|
Aspect |
Good Bots (Search Engines) |
Bad Bots (Scrapers) |
|
Purpose |
Indexing and organizing the web for search engines |
Extracting data for resale, content theft, etc. |
|
Behavior |
Transparent, identifies itself with user-agent strings |
Often disguised, mimics legitimate bots or users |
|
Respect for Robots.txt |
Follows robots.txt rules to avoid crawling restricted pages |
Ignores or bypasses robots.txt rules |
|
Server Load |
Minimal impact, avoids overloading servers |
Can overload servers with frequent requests |
|
Ethical Considerations |
Operates within ethical and legal boundaries |
Often engages in unethical or illegal activities |
|
Legal Compliance |
Complies with copyright and privacy laws |
May violate copyright laws or terms of service |
|
Respect for Web Standards |
Follows web standards (Crawl-delay, nofollow links) |
Disregards web standards and guidelines |
|
Response to Restrictions |
Stops crawling if blocked or restricted |
Attempts to bypass restrictions (IP blocks, CAPTCHA) |
|
Impact on Websites |
Positive—improves visibility and SEO |
Negative—steals content, causes server strain |
|
Examples |
Googlebot, Bingbot, Yandexbot, Baidu Spider |
Scrapers, spambots, credential stuffers |
How Crawlers Identify and Prioritize URLs?
Crawlers identify and prioritize URLs by following internal and external links found on websites. When a bot visits a page, it scans the content for URLs and adds them to its crawl queue.
The priority of URLs is determined by several factors, such as page importance, the number of internal links pointing to the page, and the website’s overall architecture similar to how targeting high-value pages works in what is B2C sales strategies.
Websites with a clean structure and fewer broken links are crawled more efficiently.
User-Agent Explanation
When a bot visits a website, it identifies itself using a User-Agent string in the HTTP request header. This string provides information about the bot, including the bot’s name and version.
Webmasters can use the User-Agent to determine which bots are visiting their site and apply specific rules for each bot (e.g., blocking bad bots or allowing good bots), which is useful when managing privacy settings like how to turn off Meta AI features.
Understanding and controlling User-Agent behavior is important for maintaining the site’s security and proper indexing.
The Crawl Budget: Why It Matters?
Crawl budget refers to the amount of resources (time, bandwidth, etc.) that a search engine allocates to crawling a website.
It determines how frequently and how many pages of your site are crawled by search engine bots. If a website has a limited crawl budget, search engines may not crawl all pages or may take longer to revisit pages, potentially delaying updates or new content from being indexed.
This can directly impact a site’s visibility in search results, especially for large websites with hundreds or thousands of pages, similar to managing budgets in paid platforms like Google Ads cost planning.
4 Factors Affecting Crawl Budget
Several factors influence a website’s crawl budget

1. Site Speed
Slow-loading pages can consume more crawl budget because search engine bots spend more time retrieving and rendering the content. Optimizing site performance ensures faster SEO crawling so bots can access more pages efficiently.
2. Errors
If a site has numerous errors (e.g., 404 pages or server errors), search engine bots may waste crawl budget trying to access broken links. Regular audits and fixing errors make crawling in SEO more efficient, ensuring that valuable time is not wasted on dead pages.
3. Internal Linking
A clear internal linking structure helps bots quickly discover important pages. Without proper linking, crawlers may miss content or follow unnecessary paths, weakening the effectiveness of your SEO crawl control.
4. Freshness of Content
Pages updated frequently are more likely to be crawled often. Fresh content signals to bots that a page is worth revisiting, which directly impacts SEO crawl frequency.
How Crawl Budget Impacts Large vs. Small Websites?
- Large Websites: For sites with hundreds or thousands of pages, crawl budget is a critical part of SEO crawling strategy. Poor management (duplicate content, broken links, slow pages) may mean that some pages never get indexed. By optimizing crawl paths and site performance, businesses can ensure that key pages receive more frequent SEO crawls.
- Small Websites: For smaller sites, crawl budget is usually less of a concern. Since they have fewer pages, crawlers can typically process the entire site easily. However, understanding what is crawling in SEO and ensuring the site is optimized for speed, error-free navigation, and strong internal linking still helps with faster indexing and better rankings.
6 Key Factors That Affect Crawling
Crawling is an essential part of SEO, but several factors can affect how effectively search engines crawl and index a website. Let’s explore the key elements that impact crawling:
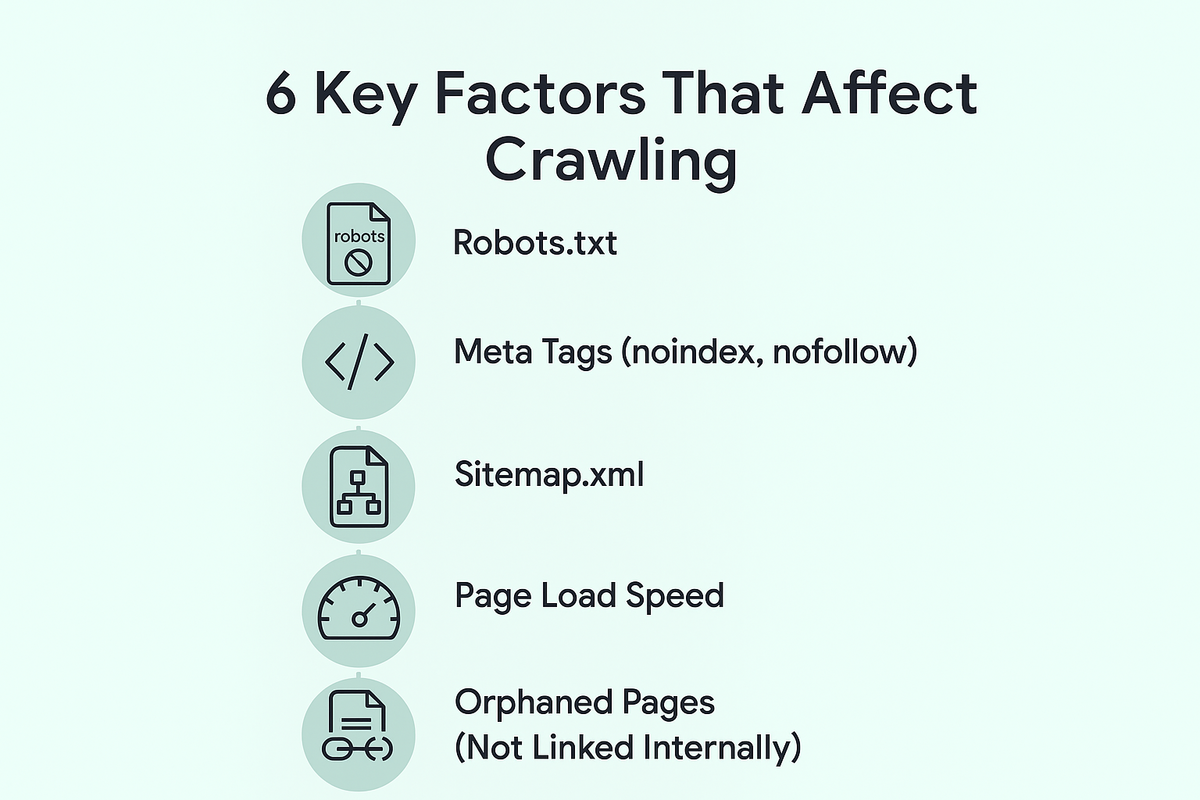
1. Robots.txt
The robots.txt file is a crucial tool for managing how search engine bots interact with your website. This file is placed in the root directory of your site and contains instructions for crawlers about which pages or sections they are allowed or disallowed from accessing.
By specifying rules in the robots.txt file, webmasters can prevent search engines from crawling duplicate content, private sections, or sensitive pages that don’t need to appear in search results. However, be cautious—misconfigured robots.txt files can block important pages from being crawled and indexed, which may conflict with noindex directives and limit visibility unnecessarily.
2. Meta Tags (noindex, nofollow)
Meta tags are HTML elements embedded within a page’s header. Two important meta tags that influence crawling are noindex and nofollow:
- noindex: Tells search engine crawlers not to index a page, meaning it won’t appear in search results.
- nofollow: Instructs crawlers not to follow the links on a page, which prevents passing link equity (ranking power) to other pages.
These tags are useful for preventing low-value or duplicate pages from affecting SEO. However, incorrectly using these tags can accidentally prevent important pages from being indexed or crawled
3. Sitemap.xml
A sitemap.xml file is a key resource for search engine bots. It acts as a roadmap, listing all important pages of a website that should be crawled and indexed.
Submitting a sitemap to search engines (e.g., through Google Search Console) can help bots discover and prioritize crawling of new or updated pages. An accurate and up-to-date sitemap ensures that no critical pages are missed, especially on large websites.
4. Page Load Speed
Page load speed significantly impacts how well search engine crawlers can crawl a site. Slow-loading pages consume more time and crawl budget, which can result in fewer pages being crawled in a given period.
Google and other search engines prioritize fast-loading sites because they offer a better user experience. Optimizing images, leveraging browser caching, and minimizing unnecessary code can help improve both page load speed and crawl efficiency.
5. Broken Links & Redirects
Broken links (404 errors) and unnecessary redirects (301 or 302) are major obstacles for search engine crawlers.
Broken links waste crawl budget and can cause bots to waste time on pages that lead nowhere. Similarly, excessive or chained redirects can confuse crawlers, making it difficult for them to follow links and discover new content.
Regular site audits to identify and fix broken links and optimize redirects are crucial for efficient crawling, especially for sites offering Content Marketing Services, where ensuring smooth navigation across landing pages can impact engagement and rankings.
6. Orphaned Pages (Not Linked Internally)
Orphaned pages are web pages that don’t have any internal links pointing to them, making them difficult for search engine bots to discover.
Even if these pages are valuable, without internal links or a sitemap, crawlers might not find them. For businesses focusing on Email Marketing Services, it’s vital to connect key campaign pages within the site’s structure to ensure they’re indexed and contributing to SEO.
Get Your Free SEO Audit Report Today!
4 Tools to Monitor and Control Crawling
Monitoring and controlling crawling is essential for maintaining a website’s SEO health.
Several tools are available to help webmasters track how search engines are crawling their site and identify areas for improvement.
Tools like Screaming Frog also allow you to inspect on-page elements, acting much like how to search for words on a page functionality but at scale for SEO audits.
1. Google Search Console
It is one of the most powerful tools for website owners. It provides detailed coverage and crawl stats, showing which pages are being crawled, which are encountering errors, and how often the bots visit your site.
It also alerts you to crawl issues, helping you optimize your crawl budget and fix problems like 404 errors or server issues.
The Crawl Stats report gives insights into how often Googlebot visits your site, the time spent crawling, and the total number of pages crawled data that complements SEO audit pricing insights to assess crawl efficiency.
2. Screaming Frog
It is another popular tool that allows you to crawl your website similarly to search engine bots. It provides a comprehensive overview of your site's URLs, identifies broken links, checks meta tags, and finds issues like duplicate content.
It’s a great tool for performing a site audit, helping you improve internal linking and optimize pages for better crawlability.
3. Ahrefs
Ahrefs offers crawl reports that provide in-depth insights into how search engines interact with your site.
These reports help identify crawling issues such as broken links, pages that are difficult to reach, and errors in your robots.txt file or sitemap.
Additionally, Ahrefs suggests improvements for your site’s structure to ensure it's fully crawlable. It also helps you track crawling efficiency and make necessary adjustments to enhance your SEO performance.
4. Semrush
Semrush also provides crawl reports that analyze search engine behavior on your site, similar to Ahrefs.
This tool identifies crawling issues and suggests optimizations to improve your site’s structure for better crawlability.
When integrated with LinkedIn Marketing Services, Semrush can enhance visibility strategies, aligning technical SEO efforts for greater impact.
Furthermore, with log file analysis tools like Loggly or GoAccess, you can examine how search engines interact with your site at a granular level, helping you make informed decisions to improve your site's SEO performance.
4 Common Crawling Issues and How to Fix Them
Common crawling issues, such as crawl errors, misconfigured robots.txt, JavaScript-rendered content, and faceted navigation, can be fixed by optimizing internal links, correcting configurations, and ensuring content accessibility for bots.
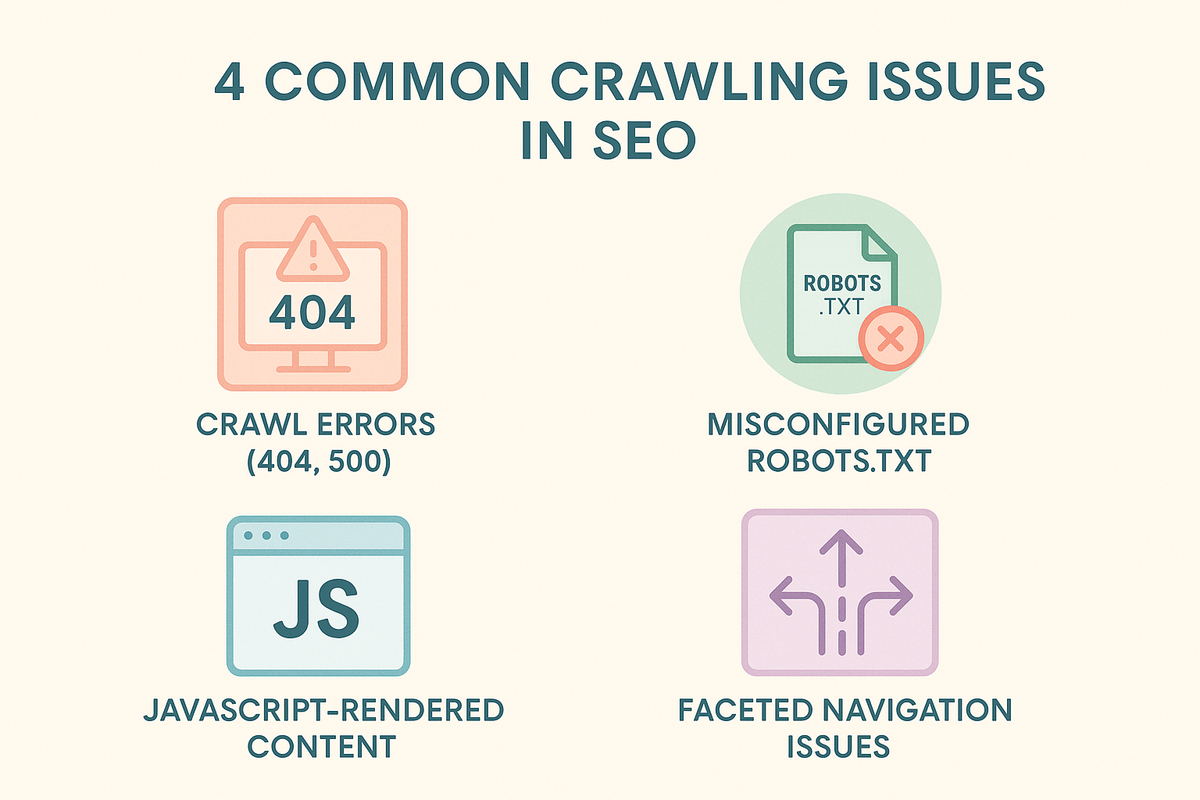
1. Crawl Errors (404, 500)
Pages that are either missing (404) or experiencing server issues (500) prevent crawlers from accessing and indexing content.
2. Misconfigured Robots.txt
Incorrect settings in the robots.txt file can block important pages from being crawled and indexed.
3. JavaScript-Rendered Content
Websites relying heavily on JavaScript may have content that search engine crawlers cannot access or index properly, a challenge often faced in complex platforms such as how does Shopify work environments.
4. Faceted Navigation Issues
Multiple versions of the same page created by filtering or sorting options lead to duplicate content, wasting crawl budget and confusing search engines.
Crawling vs Indexing vs Ranking: Know the Difference
Crawling is the discovery of pages, indexing is the storage of content for search, and ranking is the process of determining the relevance and position of pages in search results, directly influencing Google keyword ranking performance.
|
Process |
Description |
Purpose |
|
Crawling |
Search engine bots visit websites, follow links, and fetch page content. |
To discover and collect information about web pages. |
|
Indexing |
After crawling, pages are stored in the search engine’s database and analyzed for keywords, titles, etc. |
To organize and store pages in the search engine’s database for future search queries. |
|
Ranking |
Search engines evaluate indexed pages based on factors like content quality, backlinks, and user experience to assign rankings. |
To determine the position of a page in search results based on relevance and authority. |
Future of Crawling: AI and JavaScript SEO
As websites become more reliant on JavaScript, Google's crawling capabilities are evolving to keep pace. Previously, Google’s bots struggled with JavaScript-heavy sites, as they could not render dynamic content.
However, Google has improved Googlebot’s ability to execute JavaScript, allowing it to index pages with dynamically loaded content more effectively.
Server-side rendering (SSR) is playing an increasingly important role in ensuring that JavaScript-heavy websites are crawlable.
SSR generates the HTML content on the server, making it accessible to search engine crawlers immediately, unlike some client-side rendering setups that challenge even privacy-focused engines like Duckduckgo vs Google in terms of effective crawling.
This allows for faster indexing and better crawlability compared to client-side rendered sites, which can pose challenges for search engines.
Moreover, Digital Transformation Services often emphasize Core Web Vitals as a critical factor for crawlability. These performance metrics, which focus on loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability, are now a ranking factor for Google.
Additionally, Core Web Vitals are becoming a critical factor for crawlability. These performance metrics, which focus on loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability, are now a ranking factor for Google.
Websites that meet Core Web Vitals standards are not only likely to perform better in search rankings but also benefit from more efficient crawling, as fast-loading pages are easier for bots to index, improving overall SEO services and site visibility.
FAQs: What is Crawling in SEO?
1. What is Crawling in SEO?
Crawling in SEO refers to the process where search engine bots or crawlers systematically visit web pages, follow links, and gather information about the content, structure, and relationships between pages. This data is then sent back to the search engine to be indexed, making the website visible in search engine results.
2. How Does SEO Crawling Impact My Website's Ranking?
SEO crawling plays a crucial role in determining your website’s visibility in search engine results. If search engine bots can efficiently crawl your site and index its pages, your content has a higher chance of being ranked and shown to users based on search queries, increasing organic traffic.
3. What Is SEO Crawl Control, and How Can I Use It?
SEO crawl control involves managing how search engine bots crawl your website to ensure that valuable pages are prioritized and irrelevant or duplicate content is excluded. You can control crawling using tools like robots.txt, sitemaps, and meta tags, ensuring bots focus on important pages and avoid wasting crawl budget.
4. What Are Common Issues That Can Affect SEO Crawling?
Several issues can interfere with SEO crawling, including broken links, slow page load speed, misconfigured robots.txt files, and JavaScript-rendered content. Regular site audits and optimizations like fixing errors, improving site performance, and ensuring a clean linking structure can help improve crawling efficiency.
5. How Does Crawling in SEO Differ from Indexing and Ranking?
Crawling in SEO is the discovery of web pages by search engine bots. Indexing follows crawling, where the gathered information is stored and organized for retrieval. Ranking comes after indexing, where search engines evaluate indexed pages and assign them positions in search results based on relevance and quality.
6. How Can I Improve My SEO Crawl Efficiency?
To improve SEO crawl efficiency, focus on optimizing site speed, fixing errors (like 404 pages), maintaining a clear internal linking structure, and submitting an up-to-date XML sitemap. Ensuring that your content is accessible for bots and addressing issues like orphaned pages and faceted navigation will also help boost crawlability.
Conclusion
Crawling is a foundational element of SEO, as it enables search engines to discover and index the content of your website.
Without effective crawling, your pages would remain invisible in search engine results, limiting your website’s visibility and potential traffic. Ensuring that search engine bots can easily crawl and access your pages is crucial for improving your site’s ranking and overall SEO performance.
Site owners can take several key actions to optimize crawling, including maintaining a clear internal linking structure, submitting an XML sitemap, and regularly auditing for crawl errors.
Ensuring that JavaScript-rendered content is accessible and fixing issues with faceted navigation will further improve crawl efficiency, much like optimizing journeys in what is the digital marketing strategy that tracks users across the web? systems for better data collection.
Additionally, using robots.txt and meta tags strategically will help control what gets crawled and indexed.
It is essential to perform regular SEO audits to identify any crawling issues and ensure that your site remains optimized for search engines.
By doing so, site owners can stay ahead of potential problems, enhance crawlability, and ensure their content is always discoverable, keeping their site competitive in search results.









